Installing Docker and Docker Compose with Docker Engine and Docker Desktop
This article was originally published on bundleapps.io

Pick Your Operating System
You came here to ask, "how do I install Docker?" The answer can be straightforward if you're willing to accept my way, but the steps differ based on which operating system is utilized. To make things more complicated, there are a few ways to install Docker on your OS that are largely based on preference. Today I'm going to walk you through my preferred method. This isn't the only way, but I've found it to be the best way to get up and running with ease. For Ubuntu, we'll be setting up the Docker Engine. For Windows and macOS, we'll be using Docker Desktop.
Installing Docker on Ubuntu
For Ubuntu, we're going to install Docker Engine using the Docker repository. This also happens to be the recommended approach by Docker.
Set Up
Delete any prior versions if you had installed them
sudo apt-get remove docker docker-engine docker.io containerd runc
Update your system and install the necessary dependencies
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl gnupg lsb-release
For security purposes, add Docker's official GPG key. Read more about that here
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg
Set up the stable repository
echo \
"deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
$(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
That's quite a few steps, but if you followed along exactly, you should be ready to install Docker!
Installation
Install the latest version of Docker, along with its dependencies
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
Verify your install by running your first image
sudo docker run hello-world
Add your user as an admin to the Docker user group
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
Doing this last step means you no longer have to append sudo to run Docker commands!
Uninstall
Fed up with Docker on your Ubuntu box? Uninstall and remove the configuration files with the following commands.
sudo apt-get purge docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/docker
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/containerd
Installing Docker Compose on Ubuntu
Install
You must have completed the installation of Docker Engine in the steps above before you can install Docker Compose. Assuming you've done so without any errors, let's continue on!
Download the stable release of Docker compose
sudo curl -L "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.29.2/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)" -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
Unlike the installation for Docker Engine where it automatically installs the latest version, Docker Compose has to have the version manually specified. At the time of writing, the latest version is 1.29.2. The latest version can be viewed at the Compose repository release page on GitHub. Feel free to substitute the version in the command above as needed.
Make the downloaded binary executable
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
Uninstall
To remove Docker Compose, utilize the following command (assuming you installed with curl as we did above)
sudo rm /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
Installing Docker Desktop on macOS
Note that Docker Desktop comes pre-equipped with Docker Engine, Docker Compose, Kubernetes, and a few other goodies.
Installation
Intel or Apple Silicon
Depending on which chipset you have on your Mac, you'll need to install one of two versions of the Docker Desktop application. As this is a GUI application, there's not much needed other than navigating to the correct site and installing the .dmg file. Just drag and drop the Docker icon into your Applications directory.
Docker for macOS with Intel
The official link for installing Docker Desktop for macOS with an Intel chipset can be found here.
Apple Silicon
We'll also need to take a few prior steps to get Docker Desktop running with Apple Silicon. Namely, you'll need to install Rosetta 2 with the following command.
softwareupdate --install-rosetta
Afterward, install Docker Desktop for macOS with an Apple Silicon chipset from here.
Uninstall
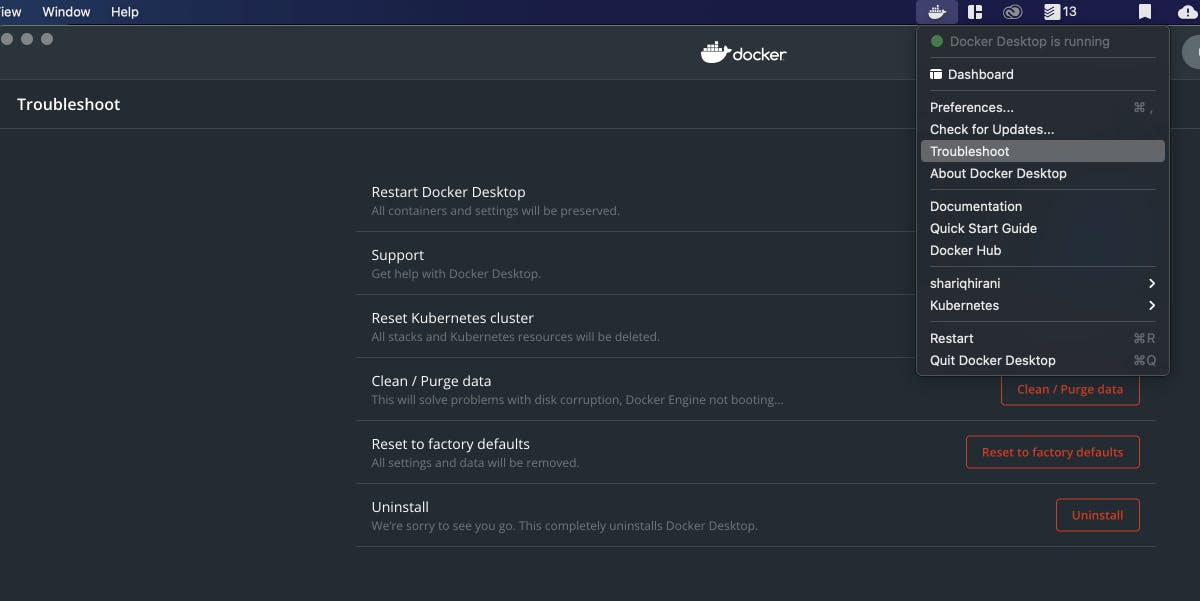
Within Docker Desktop, navigate to the menu > Troubleshoot > Uninstall. See the screenshot below.
Installing Docker Desktop on Windows and WSL2
Firstly, you will need Docker Desktop even if you want Docker to only run on WSL. This is due to the sandboxed nature of WSL.
Installation
Windows
First, you'll need to ensure that virtualization is enabled for your CPU in the BIOS. This differs amongst motherboard manufacturers and chipsets (namely Intel and AMD). A quick Google search will get you going though
The executable for Docker Desktop for Windows can be found here. It can also be found on Docker Hub. Click the installer, follow the prompts and wait for it to be downloaded
During the process, be sure to allow the prompts for Enable Hyper-V Windows Features and the Install required Windows components for WSL 2.
WSL2
You'll need to complete the steps for installing Docker Desktop on Windows BEFORE you can utilize WSL2. However, once you've completed it, feel free to come back to this section.
Enable Use the WSL2 based engine in the Docker Desktop for Windows settings and Apply & Restart
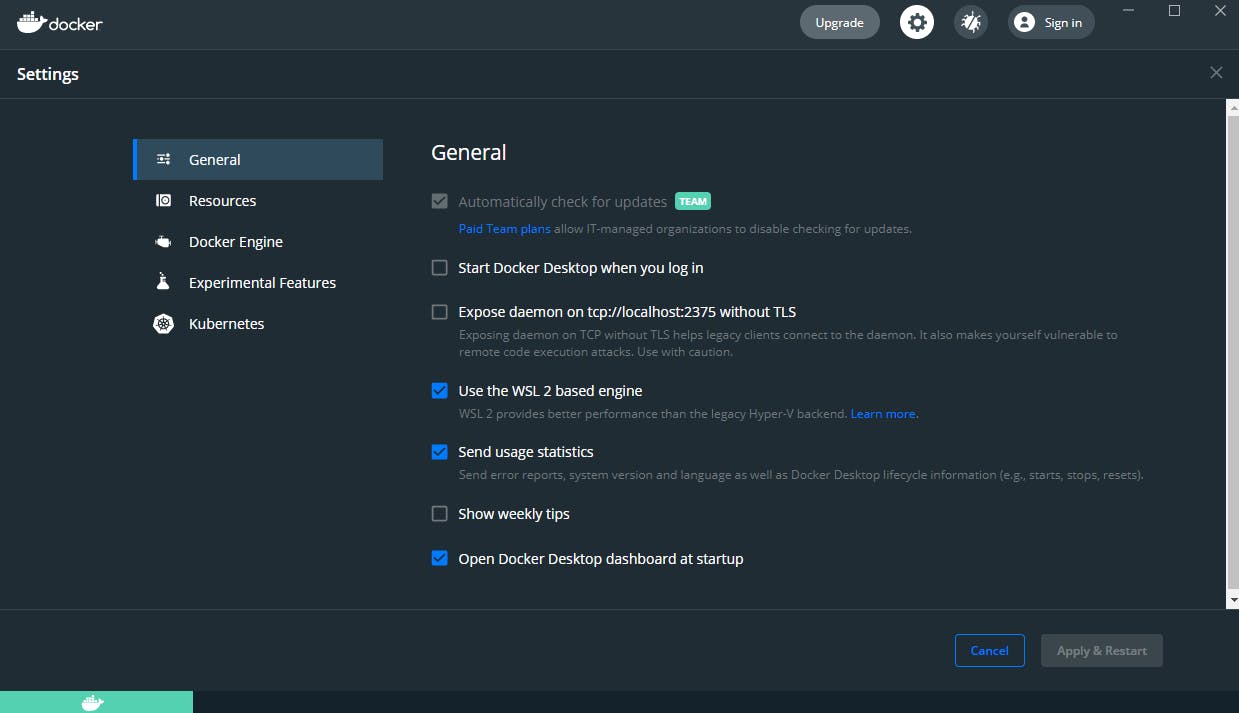
Be sure that WSL2 is set as your default and current distribution
Check the current WSL mode
wsl.exe -l -v
If not set to v2, upgrade your existing Linux
wsl.exe --set-version (distro name) 2
Set v2 as the default version
wsl.exe --set-default-version 2
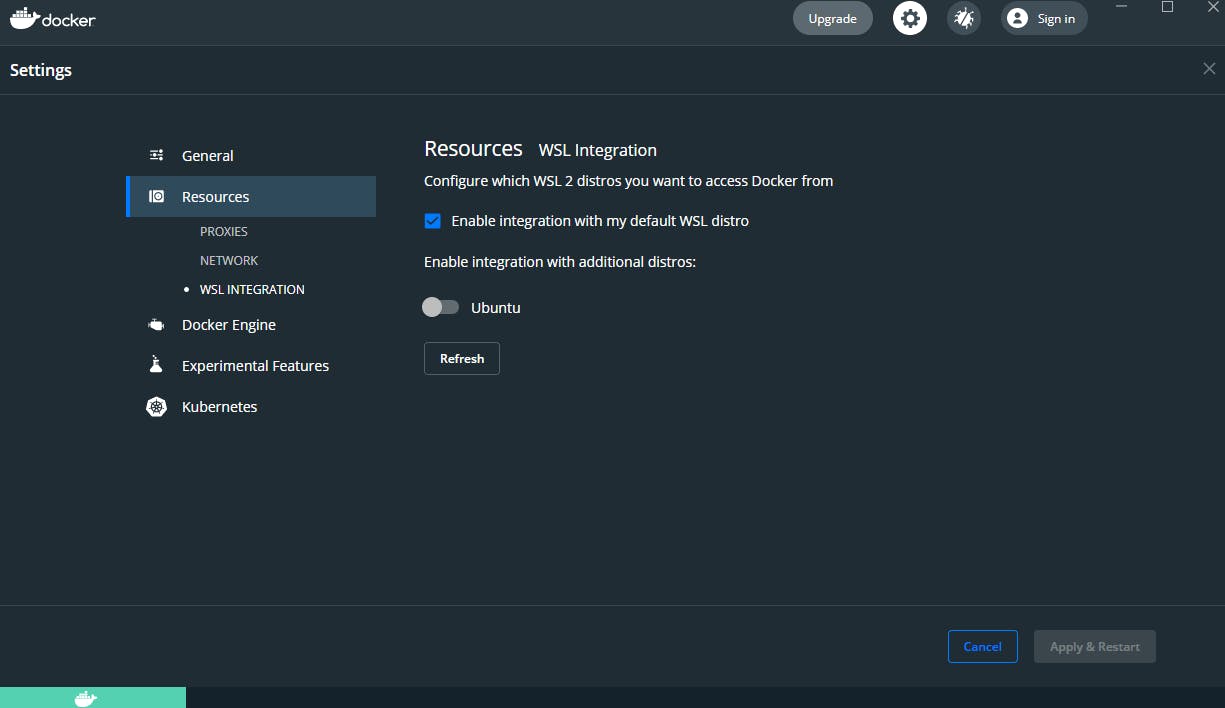
Navigate to WSL Integration and make sure Enable Integration with my default WSL distro is checked
Uninstall
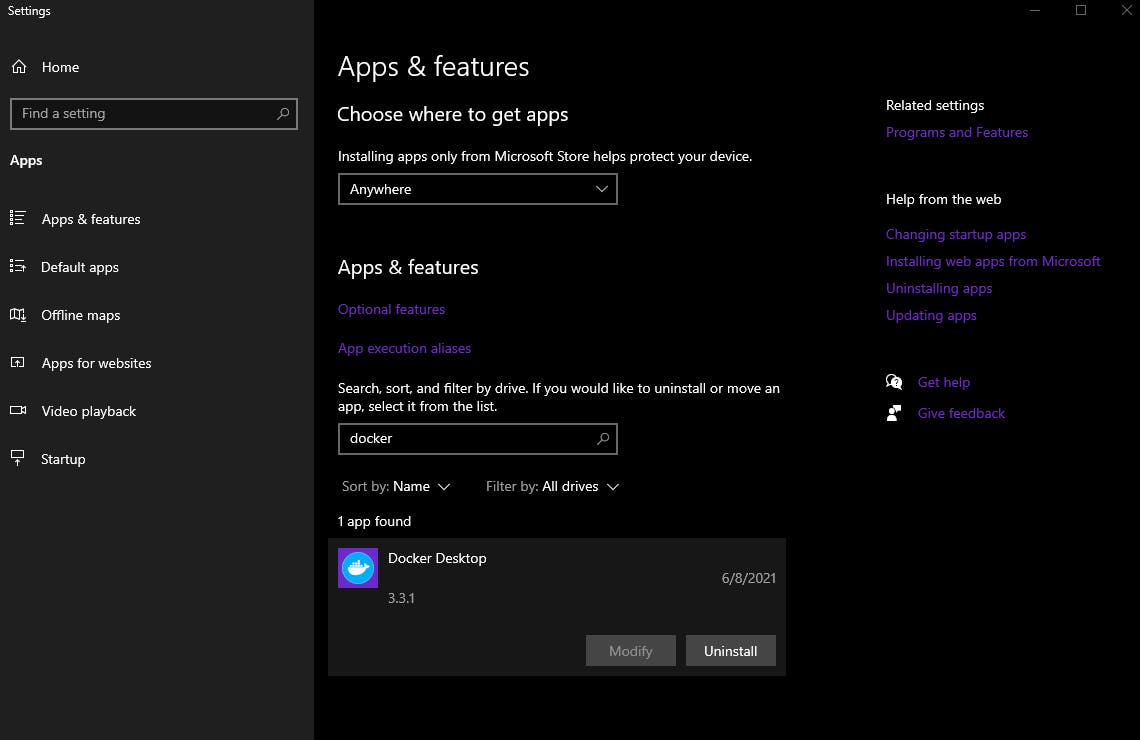
Docker Desktop can be uninstalled from the Apps & features system settings. Just search for Docker Desktop and select Uninstall. Follow the prompts.
More questions? Need help?
Be sure to check out the official documentation for Docker Engine and Docker Desktop and if you have more questions, feel free to send a message or comment below!